Zooplankton Populations

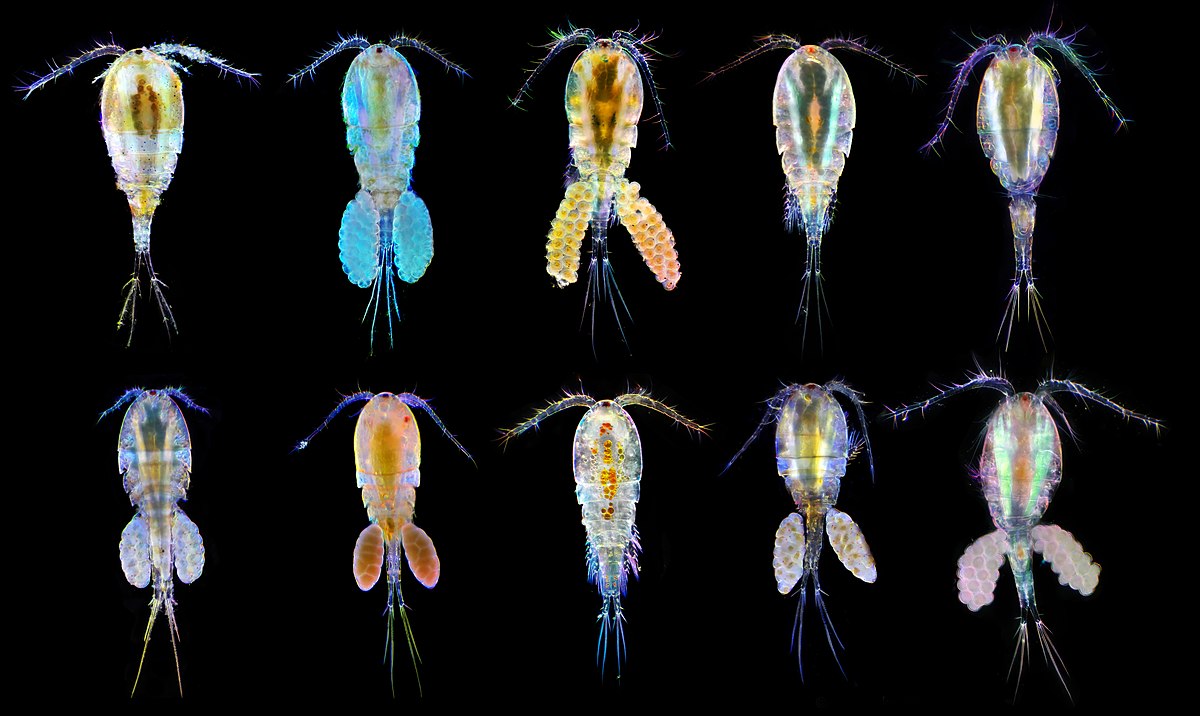
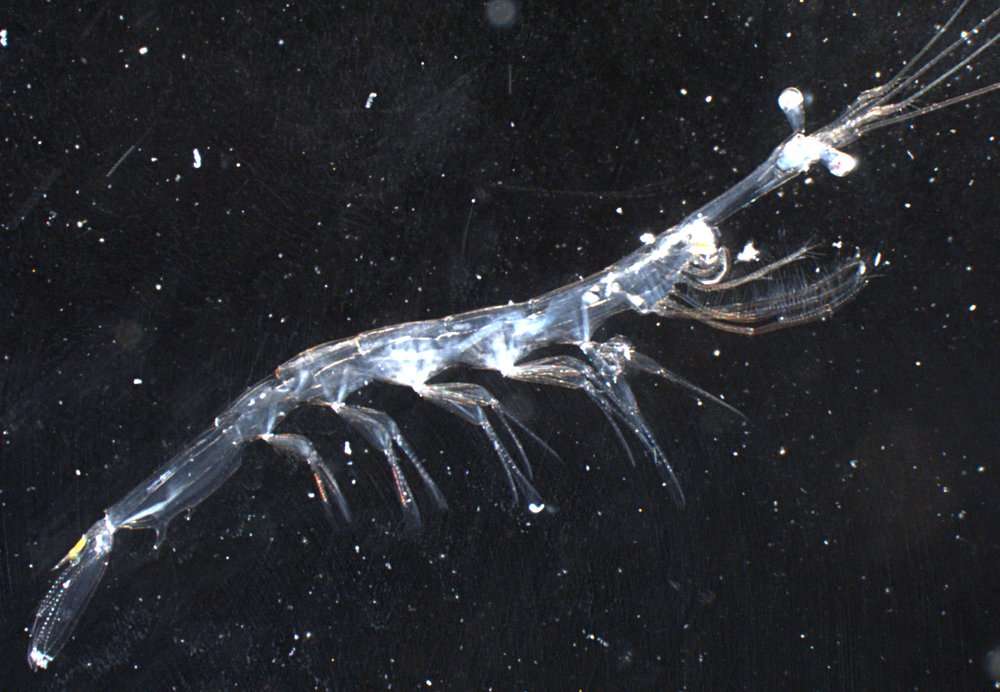
What in the world are zooplankton?
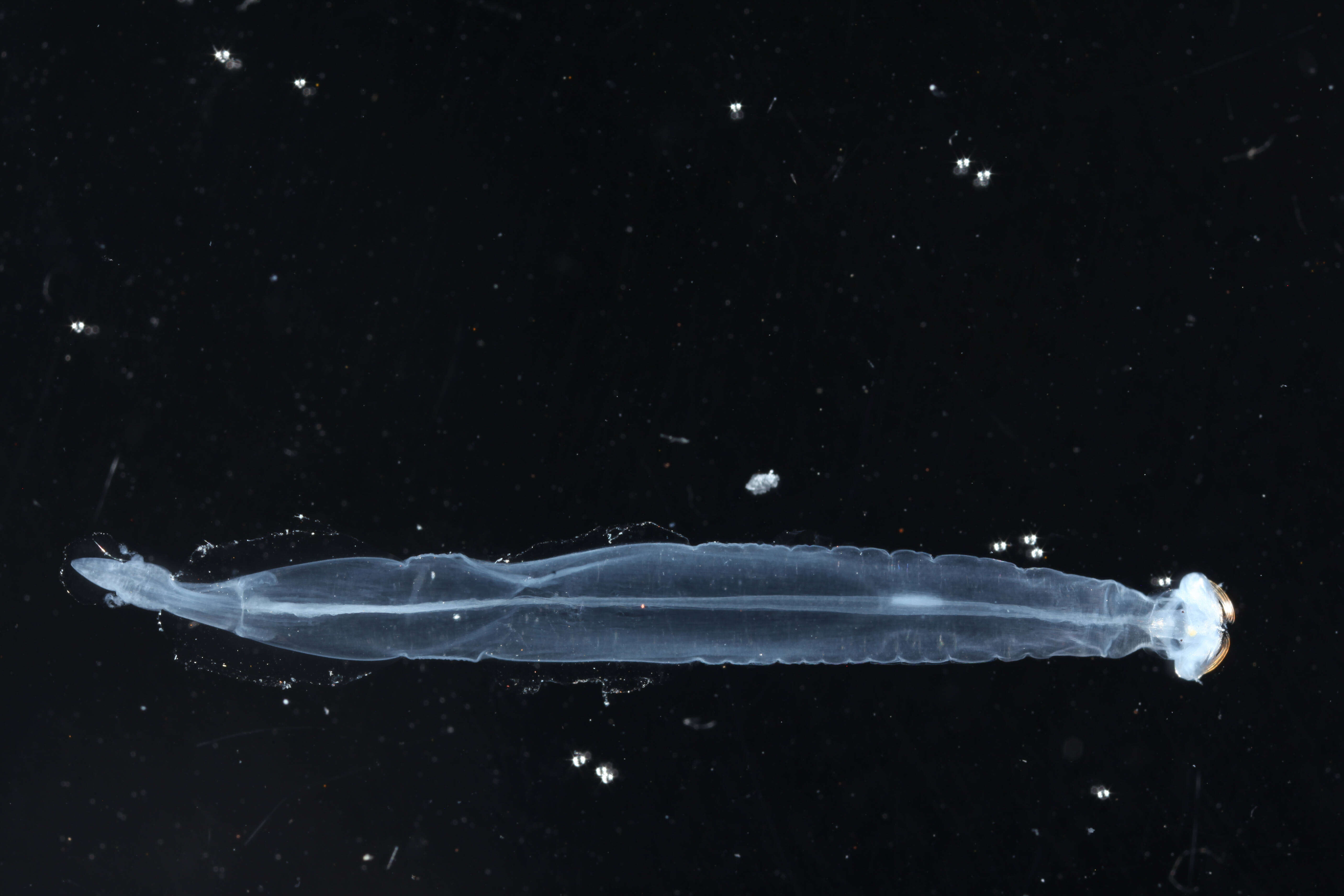
You might have heard of plankton, the name of a character in the popular cartoon Spongebob. There are two types of plankton, phytoplankton and zooplankton. The "plankton" in zooplankton is a Greek word meaning "drifter," and "zoo" comes from the Greek word meaning animal. The "phyto" in phytoplankton comes from the Greek word "fyton," meaning "plant." Together, zooplankton means "animal drifter," and phytoplankton means "plant drifter," which are broad but accurate terms. Zooplankton are tiny animals that drift in water, wherever that may take them. While they do have some ability to move on their own in the space of water they occupy, they are largely moved and affected by their environment.
Zooplankton can be found in bodies of water all around the world, including freshwater and saltwater environments. If there is a body of water, there are likely zooplankton living inside.
Why are Zooplankton important?
There are four things that make zooplankton super important:
- They consume carbon-rich organic matter like algae
- They are a food source for lots of aquatic animals
- They make great indicators of ecosystem health
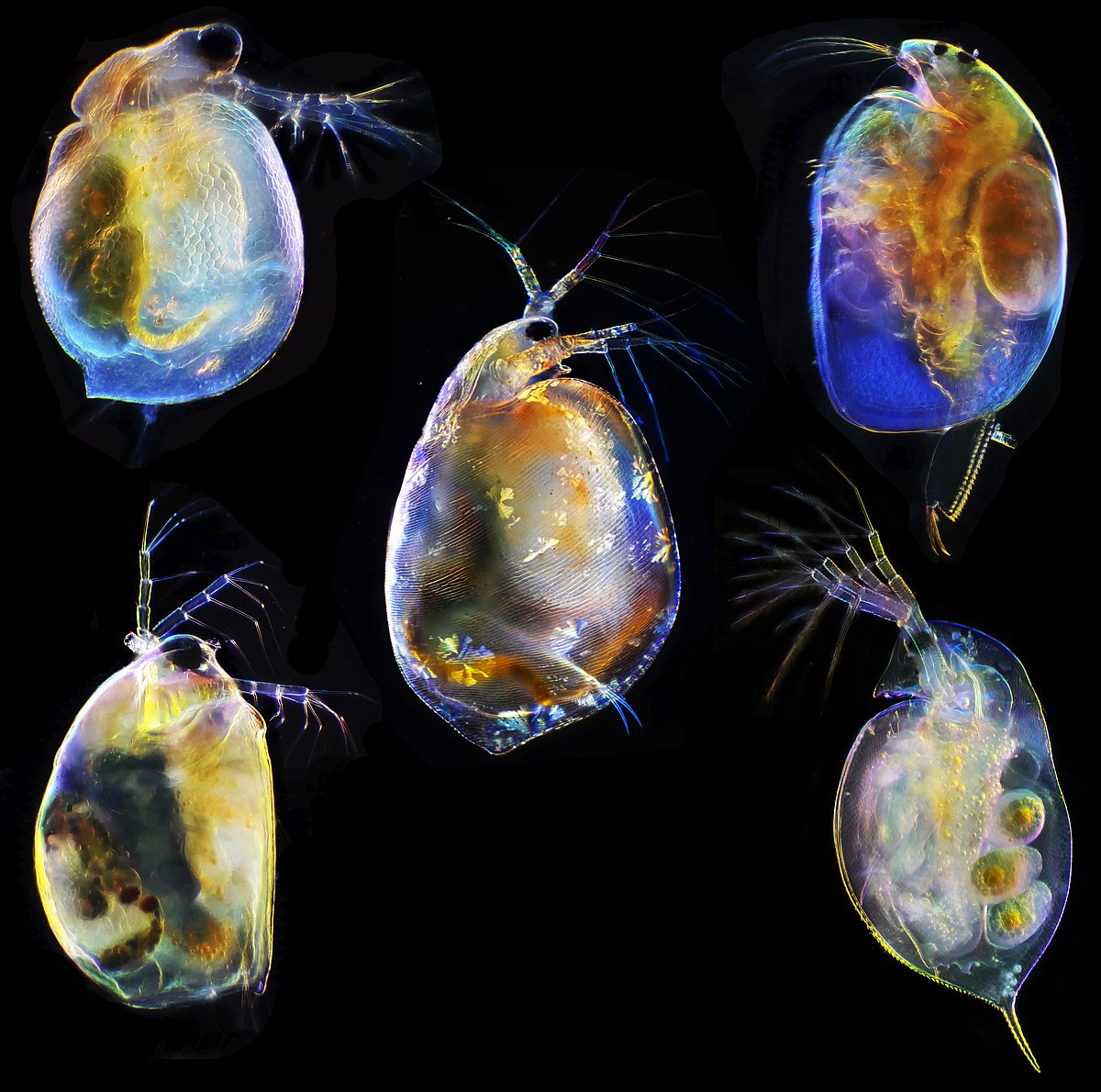
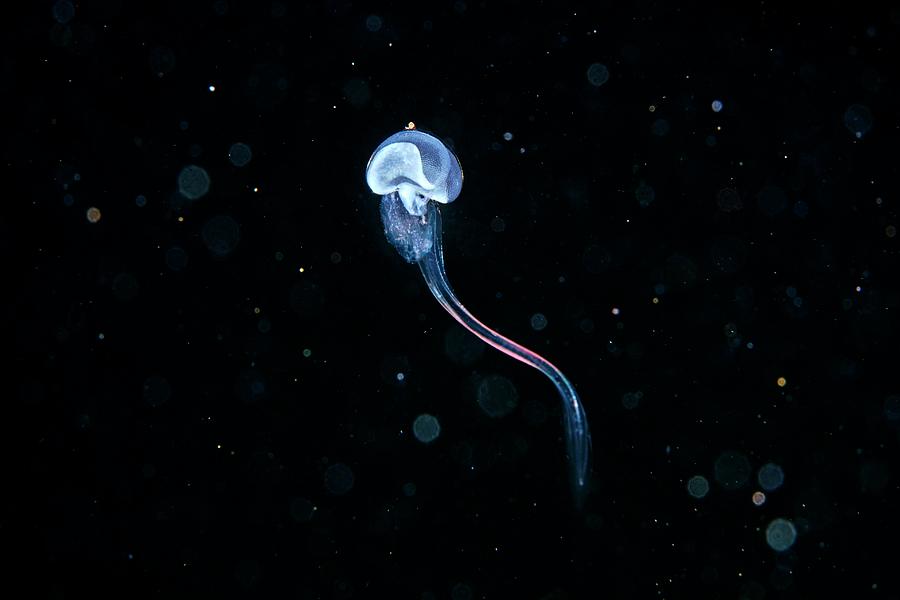
- They are very diverse!
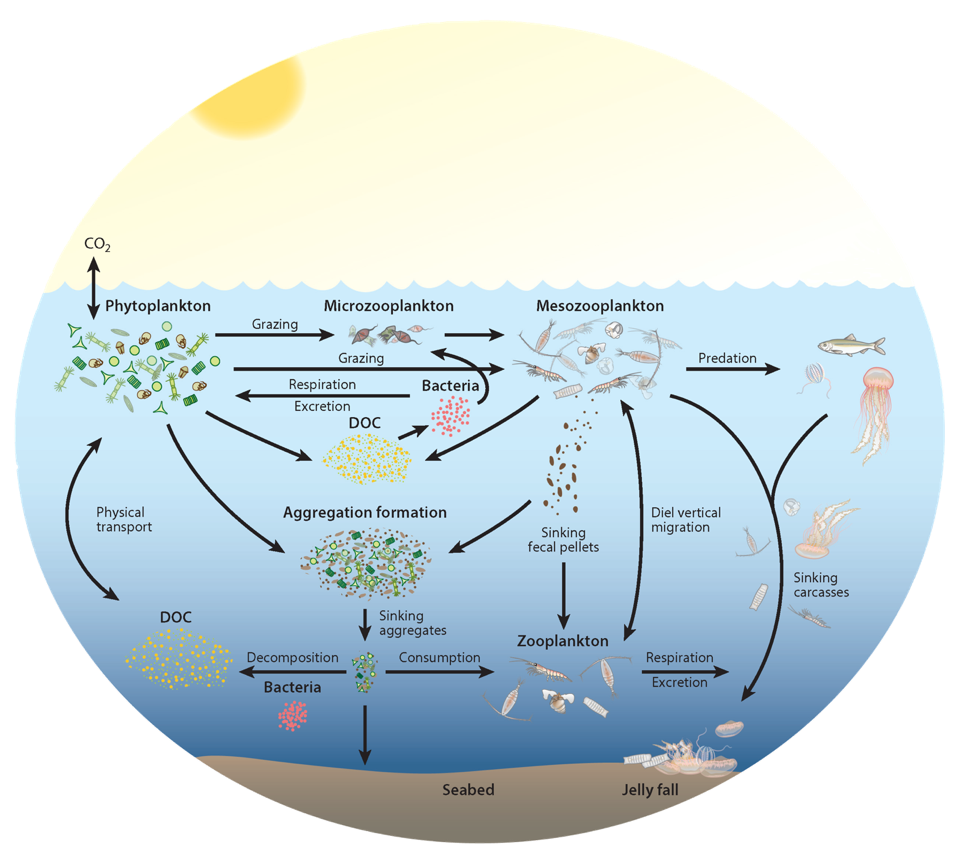
Even though this site focuses on zooplankton, let us take a moment to touch on phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are tiny plants similar in size or smaller than the examples of zooplankton above. Like other plants, phytoplankton, despite their size, absorb much carbon! Zooplankton plays an essential role in the carbon cycle by consuming the phytoplankton directly or other zooplankton that consume carbon-rich phytoplankton. Like many animals, while they are digesting, they fart and poop! The excretion of waste from zooplankton releases carbon dioxide into the water, which phytoplankton and other plants can consume. The poop sinks to the sea floor, bringing essential nutrients and removing carbon from surface water.
Many animals rely on zooplankton, including us humans. Animals like fish, birds, jellyfish, other zooplankton, and even whales survive on zooplankton as either part of their diet or as their primary food source. The importance of the food web that zooplankton provide should make their populations especially important to us humans. Humans worldwide thrive off of the fish and other aquatic creatures that exist mainly due to the presence of zooplankton. For example, many places survive off the ecotourism of blue and humpback whales, squid, herring, anchovies, and sardines serve as protein sources for human consumption. Another example is krill which are harvested and used in a variety of products like supplements as well as feed for fish farms.
Zooplankton also makes for significant indicators of ecosystem health because they are susceptible and responsive to environmental changes. Zooplankton is a broad term that includes many different types of organisms. Each organism labeled as "zooplankton" reacts differently to environmental factors such as temperature, salinity, and acidity. Some are more resistant to salt, while others are more resistant to heat. The species selected for analyzing a water ecosystem's health might change depending on freshwater or salt water, hot water or cold water, and surface water or deep water. An example would be planktonic sea snails which are very sensitive to the acidification of water, so their lack of presence or decrease in abundance in a body of water where they usually are successful as a species is an indicator of an increase in the acidity of that body of water.